Dermatologists are leveraging 3D imaging and printing technologies to enhance the precision and personalization of treatment planning and cosmetic procedures.
3D imaging and printing technologies are making significant strides in dermatology, offering solutions for treatment planning and cosmetic procedures.
These advancements are enhancing the precision, customization, and overall effectiveness of dermatological interventions. This article delves into the impact of 3D imaging and printing in the field of dermatology.
Precision in Treatment Planning

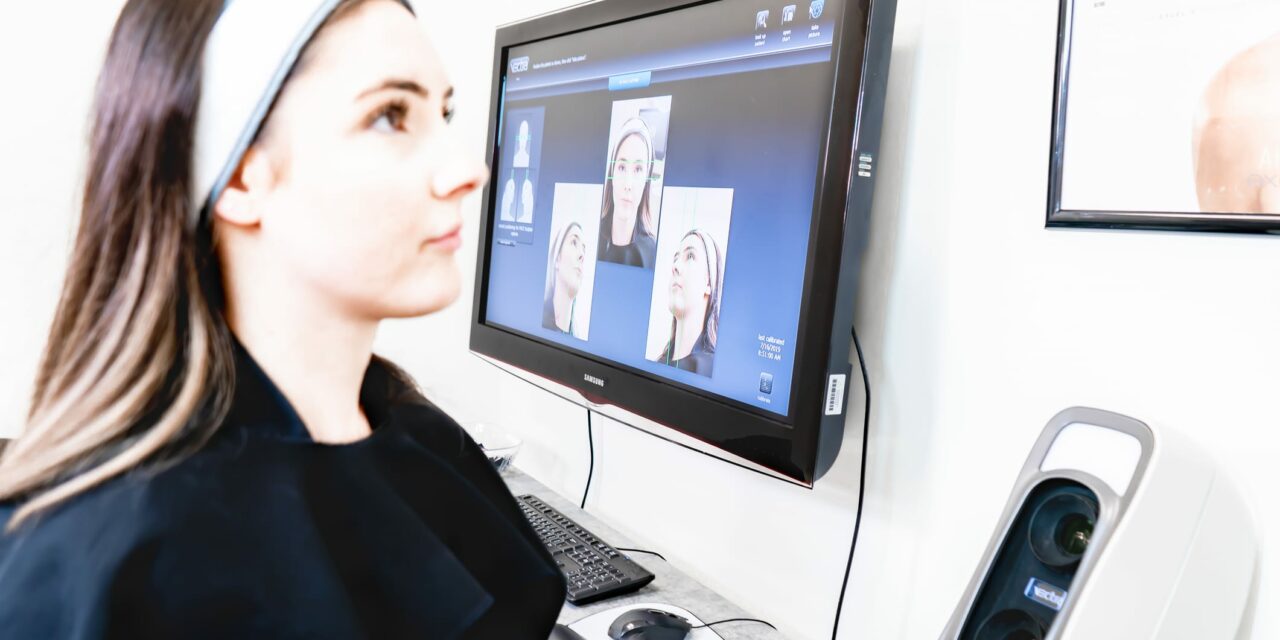
One of the most significant benefits of 3D imaging in dermatology is the precision it brings to treatment planning. By creating highly detailed, three-dimensional representations of a patient’s skin and underlying structures, dermatologists can plan procedures with unparalleled accuracy.
- Preoperative Visualization
- 3D imaging allows dermatologists to visualize the exact area of treatment before any procedure. This is particularly beneficial in complex surgeries, such as skin grafts or reconstructions, where understanding the anatomy in three dimensions is crucial. This preoperative visualization helps in predicting outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
- Custom Prosthetics and Implants
- Using 3D printing technology, dermatologists can create custom prosthetics and implants tailored to individual patients. For instance, in cases of facial reconstruction following trauma or surgery, custom implants can be designed to match the patient’s unique anatomy, leading to better aesthetic and functional outcomes.
Enhancing Cosmetic Procedures
Cosmetic dermatology has also greatly benefited from 3D imaging and printing technologies. These tools allow for more personalized and effective treatments, improving patient satisfaction and results.
- Customized Filler Injections
- 3D imaging can be used to plan and execute filler injections with high precision. By mapping the facial structure in detail, dermatologists can determine the exact placement and volume of fillers needed to achieve the desired effect. This reduces the risk of over- or under-treatment and ensures more natural-looking results.
- Patient-Specific Models for Surgery
- Before performing cosmetic surgeries, such as rhinoplasty or facelift procedures, dermatologists can use 3D-printed models to practice and refine their techniques. These models, based on the patient’s exact anatomy, allow for a more thorough preparation and can lead to improved surgical outcomes.
Clinical and Practical Applications
Beyond enhancing precision and customization, 3D imaging and printing offer practical benefits in clinical settings. These technologies can streamline workflows and improve patient communication.
- Educational Tools
- 3D models and images serve as valuable educational tools for both patients and practitioners. Dermatologists can use these tools to explain conditions, procedures, and expected outcomes to patients more effectively. This improved communication can increase patient trust and satisfaction.
- Research and Development
- 3D printing is also playing a role in dermatological research. For example, researchers can create 3D-printed skin models to study disease mechanisms, test new treatments, and develop innovative therapies. This accelerates the pace of research and brings new treatments to clinical practice more quickly.
Future Directions
The future of 3D imaging and printing in dermatology looks promising, with ongoing advancements expected to further revolutionize the field. Emerging technologies, such as bioprinting, hold the potential to create complex tissue structures, including skin, for use in transplantation and wound healing.
Final Thoughts
3D imaging and printing not only enhance treatment planning and cosmetic procedures but also improve patient outcomes and satisfaction. As the field continues to evolve, the adoption of these cutting-edge tools will likely become standard practice, further advancing the capabilities of dermatologists.
Photo 157957310 | 3d © Joycegraceweb | Dreamstime.com