Dermatology practices are adopting the latest alopecia treatments, providing new hope for patients experiencing hair loss.
Alopecia, a condition characterized by hair loss, can significantly impact a person’s self-esteem and quality of life, but, fortunately, recent advancements in medical research have led to innovative treatments that offer new hope for those affected by this condition.
This article delves into the latest treatments for alopecia, highlighting their mechanisms, effectiveness, and potential future applications.
Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors
Mechanism: Janus kinase inhibitors, or JAK inhibitors, are a class of medications originally developed for treating autoimmune diseases. These drugs work by inhibiting the activity of specific enzymes involved in the immune response, which can contribute to hair loss in conditions like alopecia areata.
Effectiveness: Recent clinical trials have shown promising results for JAK inhibitors in treating alopecia areata. For example, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine demonstrated that the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib resulted in significant hair regrowth in a majority of patients with moderate to severe alopecia areata^1. Another JAK inhibitor, ruxolitinib, has also shown effectiveness in promoting hair regrowth^2.
Future Applications: Ongoing research aims to refine the use of JAK inhibitors, focusing on optimizing dosages and minimizing side effects. There is also potential for these drugs to be used in combination with other therapies to enhance their efficacy.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
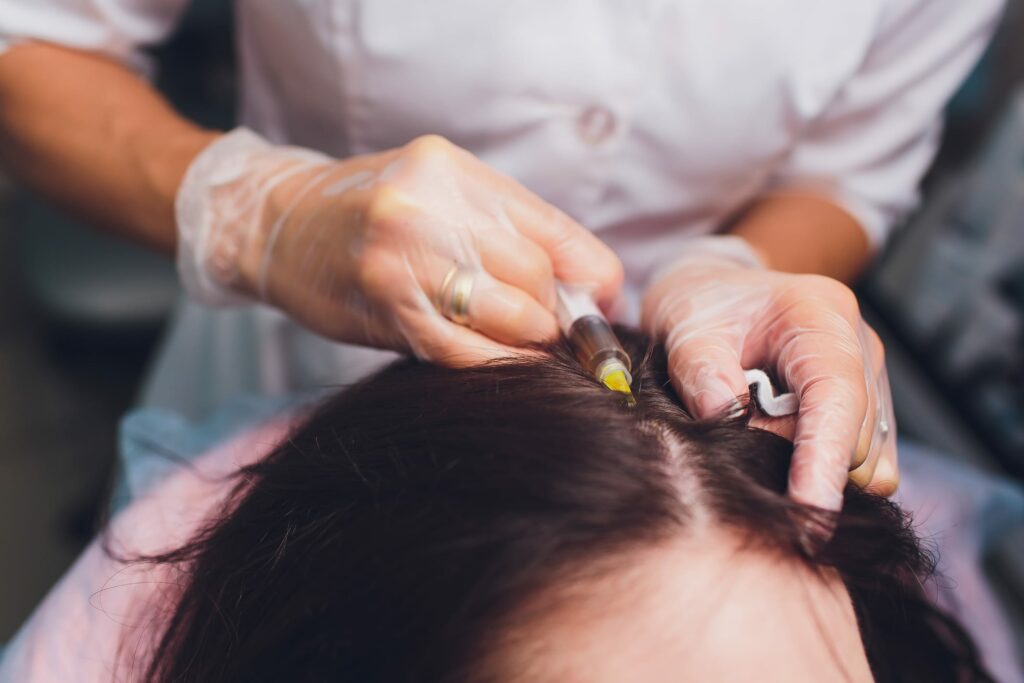

Mechanism: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy involves injecting a concentration of the patient’s own platelets into the scalp. Platelets contain growth factors that can stimulate hair follicles, promoting hair growth and improving the health of existing hair.
Effectiveness: Several studies have reported positive outcomes with PRP therapy for various types of alopecia. A systematic review published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology found that PRP therapy significantly improved hair density and thickness in patients with androgenetic alopecia^3. PRP has also been used successfully to treat alopecia areata and scarring alopecia.
Future Applications: Researchers are exploring ways to enhance PRP therapy, such as combining it with other treatments or using advanced techniques to increase the concentration of growth factors. Personalized PRP formulations based on individual patient profiles are also being investigated.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
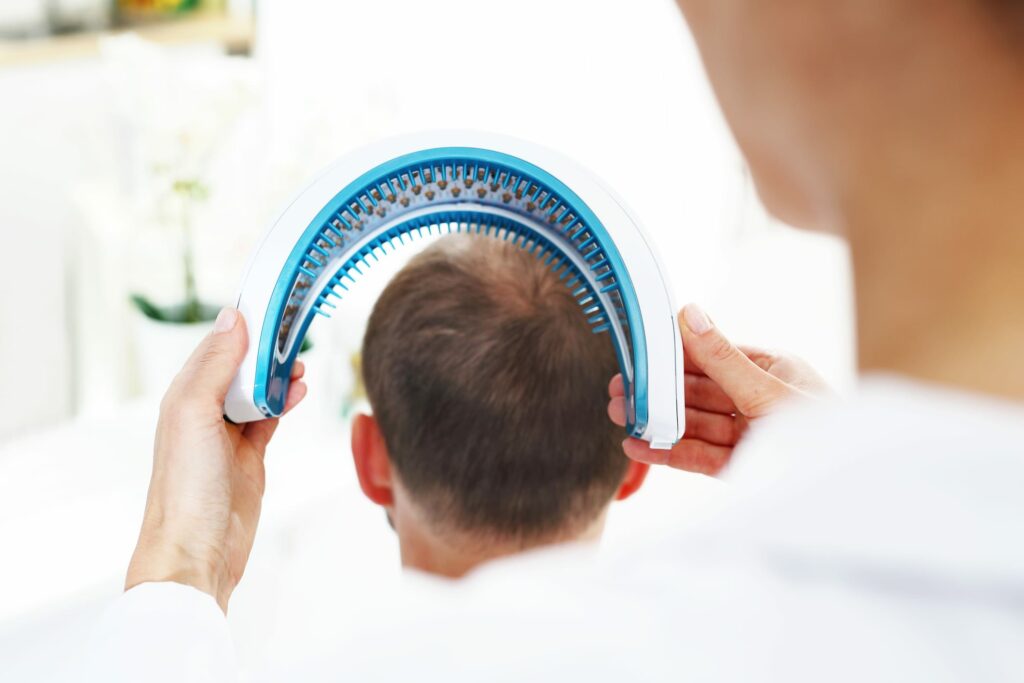

Mechanism: Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) uses red or near-infrared light to stimulate hair follicles, promoting hair growth and preventing further hair loss. The light energy is absorbed by cells, which can enhance cellular activity and improve hair follicle function.
Effectiveness: LLLT has been shown to be effective in treating androgenetic alopecia and other forms of hair loss. A randomized controlled trial published in Lasers in Surgery and Medicine demonstrated that LLLT significantly increased hair density in patients with androgenetic alopecia compared to a placebo group^4.
Future Applications: Advancements in LLLT devices, such as the development of more powerful and efficient lasers, are expected to improve treatment outcomes. Combining LLLT with other therapies, such as topical medications or PRP, is also being explored to enhance its effectiveness.
Stem Cell Therapy
Mechanism: Stem cell therapy involves the use of stem cells to regenerate hair follicles and promote hair growth. These cells can differentiate into various cell types, including those that make up hair follicles, and can secrete growth factors that stimulate hair growth.
Effectiveness: Early-stage clinical trials have shown that stem cell therapy can be effective in treating alopecia. For instance, a pilot study published in Stem Cells Translational Medicine found that patients treated with stem cell injections experienced significant hair regrowth^5.
Future Applications: Stem cell therapy holds great promise for the future of alopecia treatment. Ongoing research aims to improve the delivery methods and effectiveness of stem cell treatments. Combining stem cells with other therapies, such as PRP or gene therapy, is also being investigated to enhance their regenerative potential.
Final Thoughts
The latest innovations in alopecia treatment offer new hope for individuals with hair loss. From JAK inhibitors and PRP therapy to LLLT and stem cell therapy, these emerging therapies are paving the way for more effective and personalized treatment options. As research continues to advance, the future looks promising for those affected by alopecia.
References
- King, B., et al. (2014). “Tofacitinib for the Treatment of Alopecia Areata.” New England Journal of Medicine.
- Mackay-Wiggan, J., et al. (2016). “Ruxolitinib for Alopecia Areata and Other Inflammatory Diseases.” Journal of Clinical Investigation.
- Gentile, P., et al. (2015). “Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy in Androgenetic Alopecia.” Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Avci, P., et al. (2014). “Low-Level Laser (Light) Therapy (LLLT) for Treatment of Hair Loss.” Lasers in Surgery and Medicine.
- Kim, W., et al. (2017). “Stem Cell Therapy for Hair Regrowth: A Review.” Stem Cells Translational Medicine.
Photo 190745569 © Alona Siniehina | Dreamstime.com