Advancements in imaging technologies, from dermoscopy to optical coherence tomography, are improving dermatological diagnostics by enhancing accuracy and early detection of skin conditions.
Dermatology has seen significant advancements in imaging technologies over recent decades, revolutionizing the field’s diagnostic capabilities. From the traditional dermoscopy to the cutting-edge optical coherence tomography (OCT), these technologies enhance the precision, accuracy, and early detection of various skin conditions.
This article delves into the evolution of these imaging technologies, their applications, and the impact on clinical practices.
Dermoscopy: The Foundation of Modern Dermatological Imaging
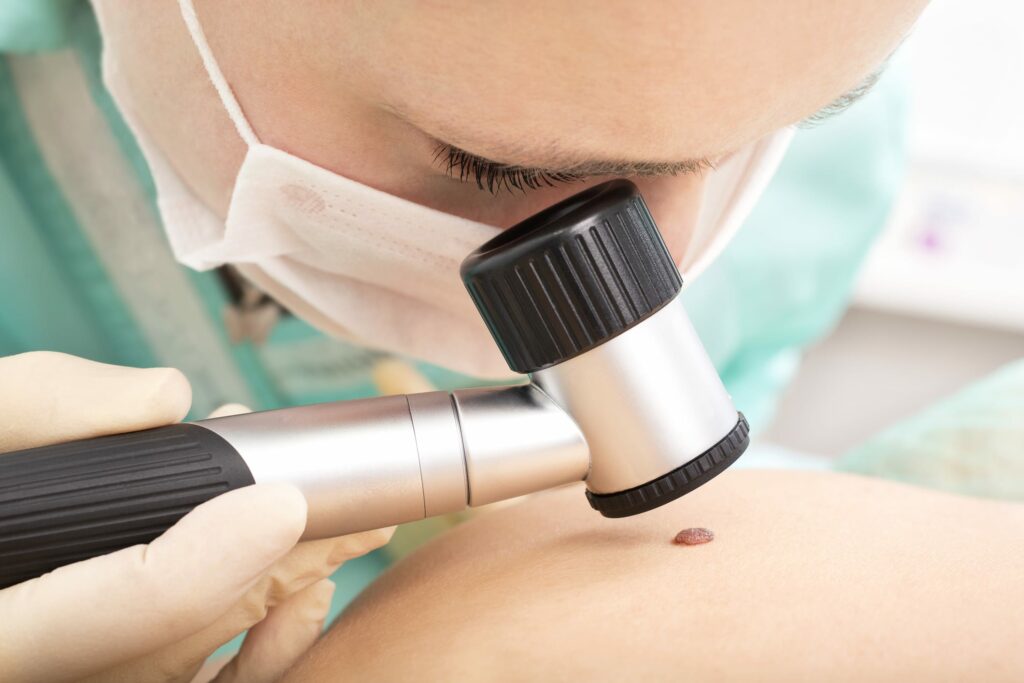
Dermoscopy, also known as dermatoscopy or epiluminescence microscopy, is a non-invasive diagnostic method that allows dermatologists to observe skin lesions with greater clarity than the naked eye. By using a dermatoscope, clinicians can magnify skin structures up to ten times, revealing subsurface patterns and colors indicative of various dermatological conditions.
Dermoscopy has become an essential tool in the early detection of melanoma and other skin cancers, significantly improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing the need for unnecessary biopsies (Oxford Academic) .
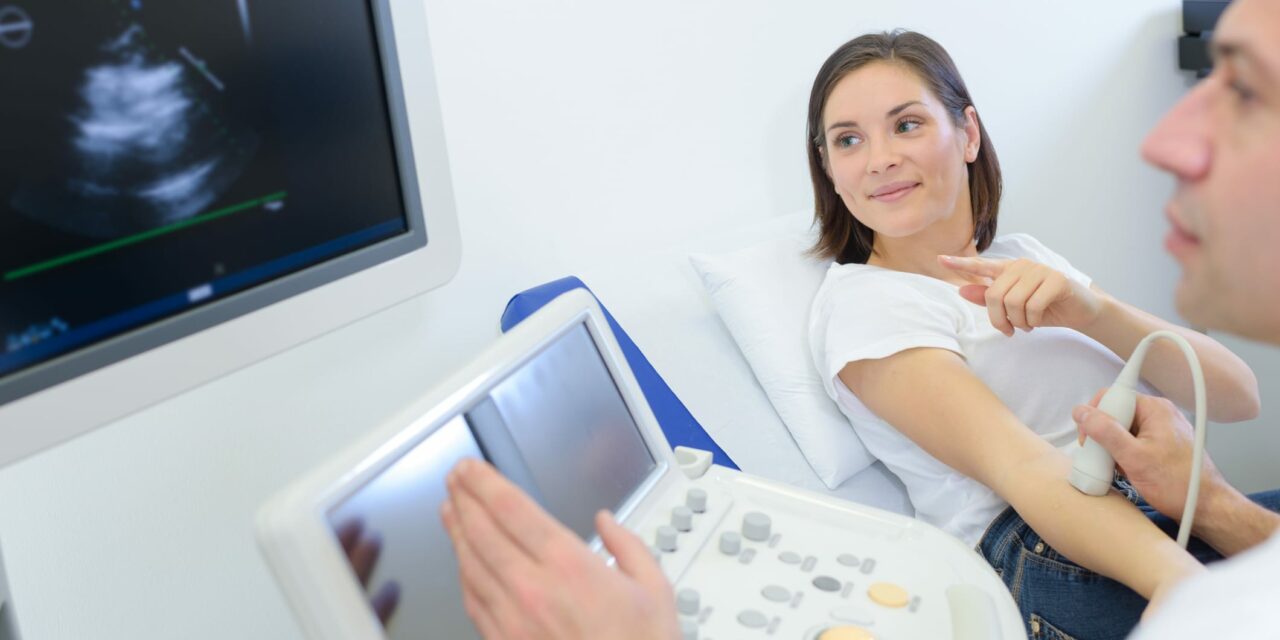
High-Resolution Ultrasound: Enhanced Depth Visualization
High-resolution ultrasound offers another layer of diagnostic capability by providing real-time imaging of the skin and underlying tissues. Unlike dermoscopy, high-resolution ultrasound allows for the assessment of the skin’s deeper layers, making it invaluable for evaluating tumors, cysts, and other subcutaneous abnormalities. This non-invasive technique is particularly useful in monitoring treatment responses and guiding surgical interventions (Oxford Academic).
Reflectance Confocal Microscopy: Cellular-Level Insights
Reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) has emerged as a powerful tool for in vivo imaging at the cellular level. RCM provides real-time, high-resolution images of the skin’s epidermis and superficial dermis, allowing for the detailed examination of skin lesions (Oxford Academic).
This technology is particularly effective in distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions, reducing the need for invasive biopsies. Its ability to provide cellular-level detail makes RCM a critical tool for diagnosing skin cancers and other dermatological disorders.
Optical Coherence Tomography: A New Era of Precision Imaging
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) represents one of the most advanced imaging technologies in dermatology today. OCT uses light waves to capture micrometer-resolution, cross-sectional images of the skin, similar to ultrasound but with much higher resolution (Oxford Academic).
This technology allows for the visualization of skin architecture in three dimensions, providing detailed information about the skin’s microstructures. OCT is particularly useful in diagnosing non-melanoma skin cancers, assessing wound healing, and evaluating inflammatory skin diseases .
Comparative Analysis: Strengths and Limitations
While each imaging technology has its strengths, they also have limitations. Dermoscopy is highly effective for superficial lesions but lacks depth penetration. High-resolution ultrasound provides excellent depth visualization but has lower resolution compared to other methods. RCM offers unparalleled cellular-level detail but is limited to superficial layers. OCT combines high resolution with depth penetration, making it highly versatile, but it is less effective for detailed cellular imaging compared to RCM.
Integration of Imaging Technologies in Clinical Practice
The integration of these advanced imaging technologies in clinical practice has transformed dermatological diagnostics. By combining dermoscopy, high-resolution ultrasound, RCM, and OCT, dermatologists can achieve a comprehensive evaluation of skin conditions, leading to more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
The use of these technologies also reduces the need for invasive procedures, enhancing patient comfort and outcomes (Oxford Academic) .
The Future of Dermatological Imaging
Looking ahead, the future of dermatological imaging is promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at further enhancing the capabilities of existing technologies and introducing new innovations. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are expected to play a significant role in this evolution, enabling automated image analysis and improving diagnostic accuracy.
These advancements will continue to shape the field of dermatology, offering new possibilities for early detection, treatment, and monitoring of skin diseases.
Empowering Dermatologists with Advanced Imaging
Advanced imaging technologies have undeniably revolutionized dermatological diagnostics, providing tools that offer detail, depth, and accuracy. From the foundational dermoscopy to the state-of-the-art OCT, these innovations empower dermatologists to make more informed clinical decisions, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.
Photo 101669028 © Auremar | Dreamstime.com